Understanding the Importance of a Motor Vehicle Record Policy

Motor Vehicle Records (MVRs) are important because they provide a “snapshot” of a driver’s recent history and can help determine driving privileges within your organization.
An essential ingredient of an organization’s driver safety program involves evaluating drivers’ Motor Vehicle Records (MVRs). Without this basic step, members and the organization could be put at risk with an unsafe driver on the road.
The following chart from July 2018 presents the specific driving behaviors that are most predictive of future crash involvement:
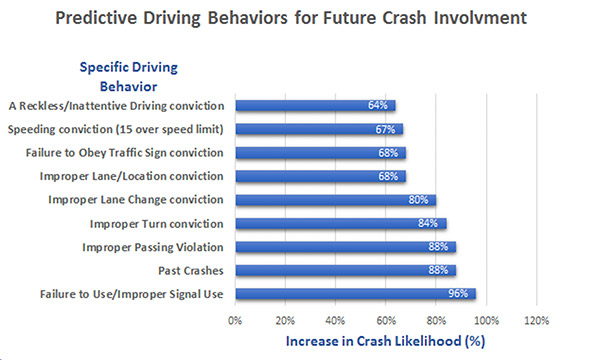
Data source: The American Transportation Research Institute - Specific Driving Behaviors Most Predictive of Future Truck Crash Involvement
MVRs are important because not only will they provide peace of mind, but they also provide key insights into an employee's driving history, accidents, convictions, moving violations and suspensions. Typically, drivers who have multiple violations are more likely to be involved in future accidents. Allowing employees who have poor driving records to operate your organization’s vehicles increases your liability exposure. MVRs should be examined prior to the start of employment and annually thereafter.
It is important to create and implement a formal MVR policy to ensure that the evaluation and driver screening process is administered consistently. An MVR policy should address the following factors:
Who Is Subject to the Policy?
Any staff member who operates a vehicle for the organization should be covered, including the following:
- Employees who regularly rent cars during business trips
- Employees frequently attending seminars and conferences
- Employees who run errands with company vehicles
- Part-time and temporary employees, as well as interns
- Volunteers, coaches, board members and elected officials
- Family members who are permitted to drive company vehicles
When Must an MVR Be Obtained?
- Any prospective employee who will be covered under the MVR policy prior to commencing driving duties must obtain an updated MVR.
- Current employees who drive or those moving into positions that involve driving should have an MVR at least annually.
- MVRs should also be obtained after an accident occurs or after a call-in report/complaint has been received.
How Should a Driver’s History Be Evaluated?
MVRs can usually be obtained from the state driver licensing office or a third-party vendor that provides consumer reports. When evaluating MVRs, you should evaluate a three-to-five year driving history.
Drivers located in the “POOR” history range should not be allowed to drive for an organization until their history improves.
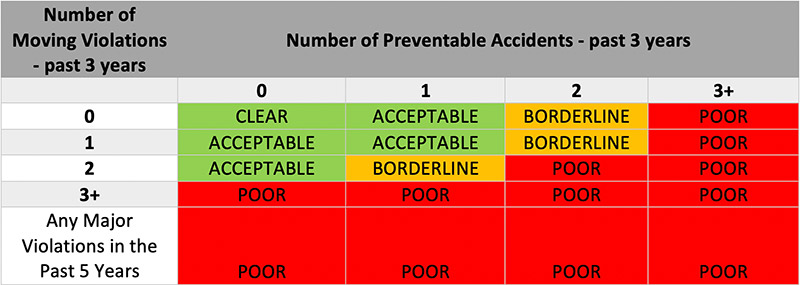
*Non-preventable accidents are when there was absolutely nothing the driver could have done to prevent the accident.
*Preventable accidents are any accident that does not classify as non-preventable.
Examples of Major Violations
- Leaving the scene of an accident
- Driving under the influence of drugs or alcohol
- Racing or excessive speed (greater than 20 mph over the speed limit)
- Reckless, negligent or careless driving
- Felony, homicide or manslaughter involving the use of a motor vehicle
- License suspension or revocation resulting from accidents or moving violations
- Following too closely or tailgating
- Erratic lane changing
- Attempting to elude a police officer
Examples of Minor Violations
- Speeding less than 20 mph over the speed limit
- Failure to obey sign
- Failure to yield
- Illegal turn
Examples of Non-Moving Violations
- Parking tickets
- Motor vehicle equipment violations
- Failure to have a valid operator’s license available where one exists
Hiring Considerations
- Consideration of whether job applicants who have borderline or poor MVRs should be hired for driving positions or allowed to drive for business purposes
- Consideration of whether current employees who have borderline or poor MVRs should have their driving responsibilities suspended or if they should be reassigned to non-driving positions until after their driving records become acceptable
- Adequate documentation guidelines on record retention
Documentation
Guidelines provided in the MVR policy should include retention of applicants, release forms, the actual MVR, annual certificates of violations, annual MVR reviews, and warnings and corrective action taken.








.jpeg?sfvrsn=dbf923b1_1)




.jpeg?sfvrsn=c50521b1_1)
